Blog
E-health startups, medical businesses, and healthcare professionals may find it challenging to implement SaMD solutions due to data privacy concerns and strict regulations. By clarifying regulatory requirements, integration strategies, and security practices, we aim to enablee medical stakeholders to make informed decisions about their SaMD products.
Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) has become an increasingly popular area of software
development in recent years. And today, particular solutions are widely integrated into the
existing hardware medical devices created to ensure patient safety.
In addition, the appearance of new technologies has enabled SaMD to evolve in terms of its capabilities
and use cases for various patient populations. But at the same time, Software as a Medical Device
remains quite a new category transforming the international medical device field. Thus, the relevant
regulatory requirements have also emerged over time.
That makes it crucial for medical care startups considering developing SaMD products and investors
interested in supporting SaMD companies to learn about Software as a Medical Device in detail.
Apart from analyzing what SaMD is, they should also understand how smart device manufacturers
work to promote digital health in the modern competitive market.
Below, we will explore the nature of SaMD software, its key advantages, examples, and trends,
and also take a look at the current medical device regulations.
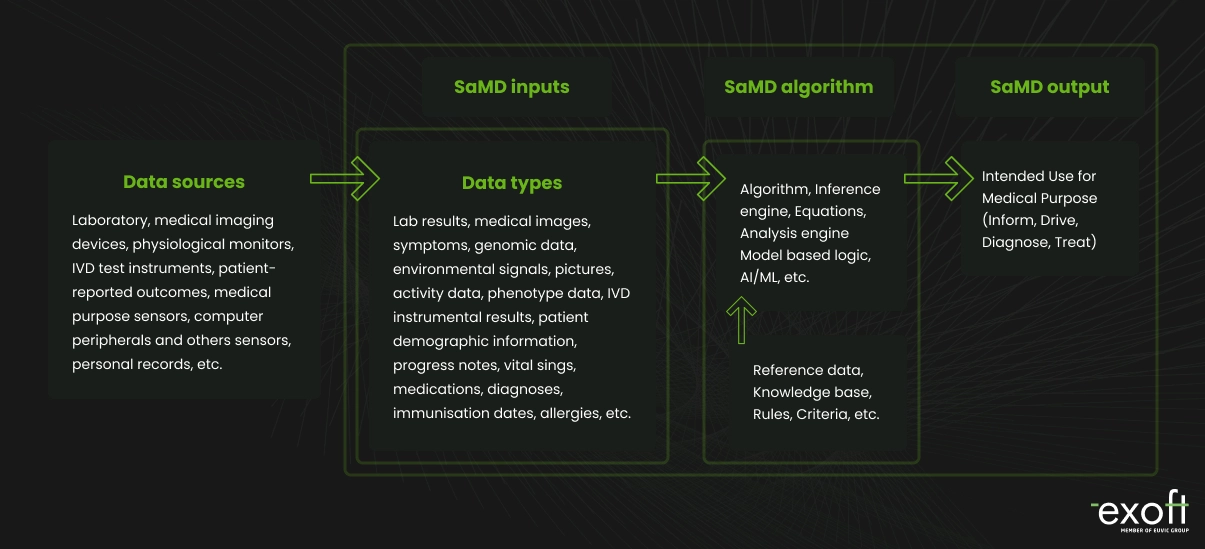
What is software as medical device (SaMD)?
According to the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF)
and their Software as a Medical Device working group, SaMD is
“software intended to be used for one or more medical purposes that perform these purposes
without being part of a hardware medical device.” Meanwhile, the Food and Drug
Administration (FDA) considers SaMD “software that meets the definition of a device in 181
section 201(h) of the FD&C Act and is intended to be used for one or more medical purposes
without being part of a hardware device.”
In other words, based on the mentioned definitions, SaMD can run independently of your specific
medical device or hardware. Thus, you may find a clear line between SaMD and other types of modern
product development methodology solutions.
Benefits of SaMD
SaMD creates several critical advantages for all stakeholders, including medical device
software companies, their investors, healthcare organizations and facilities, and, of
course, patients. For example, rapid data collection and analysis are among the key pros
offered by SaMD development. That is because it outpaces the capabilities of human employees
dealing with clinical management and treatment decisions.
It means that clinics and hospitals can gather and assess medical conditions and changes in basic
monitoring information quickly, which helps improve health outcomes. Therefore, there is a chance
to expand SaMD to be used for various medical purposes and management and facilitation of treatment
regarding multiple public health problems.
For instance, patient vital signs can change dramatically over time. But the patients and their
healthcare providers may notice no relevant symptoms. Fortunately, the proper Software as a Medical
Device solution provides real-time monitoring of conditions and alerts doctors about any patterns
that they must investigate. Thus, utilizing a particular hardware medical device can make a significant
difference. That is because patients can receive the necessary care and prevent disease before
becoming ill, which promotes better health outcomes.
Moreover, the ability of medical device software to quickly collect information also facilitates
obtaining critical feedback and conducting analysis. So, such an approach also results in faster
improvements and innovations. Meanwhile, SaMD brings high-quality information as healthcare organizations
gather it directly from the source and can get it easily at scale. And clinicians can find valuable
insights more quickly, which makes utilizing medical devices advantageous for treatment recommendations
and overall treatment trajectory.
With an innovative data-gathering feature, SaMD has become one of the most popular sources for
Clinical Decision Support. That covers different SaMD tools and medical software systems collecting
and analyzing data, noting trends, and providing alerts or prompts to doctors. Many medical device
companies develop these systems and equip them appropriately to support physicians in their healthcare
decisions and enable them to take action. But such clinical decision support tools are not final
decision-makers.
In addition, the existing strict medical device regulation is also an important benefit, although
SaMD developers and investors may disagree with this opinion. But since current applicable regulations
mean that not every company is ready to spend time and effort on the SaMD development process,
you will face a limited field of competitors.
Ultimately, because of such strict medical device SaMD regulations, companies that bring their
products to market are considered as those who have thoroughly developed and tested these tools.
That allows for boosting the confidence regarding device efficiency among doctors and increasing
their desire to utilize a particular hardware device along with other medical device solutions,
mHealth mobile apps, and
various medicinal products they rely on. Lastly, that increases your SaMD software’s chances
to become accepted under governmental large-scale programs.
How is SaMD regulated
Of course, medical device SaMD development requires more strict regulatory compliance
compared to other software products that healthcare providers indirectly use for proper care
delivery. It means that SaMD manufacturers need to maintain specific rules and collect data
throughout the whole medical device’s product lifecycle. That is because the existing
regulatory authorities aim to ensure the device’s information integrity. In such a case,
issues like privacy and security of SaMD software are integral components of the regulatory
process.
You may realize that SaMD development is treated a bit differently by various medical device
regulators, even though the International Medical Device Regulators Forum has intended to bring
more harmonization. Traditionally, like other medical devices, SaMD classification depends on
risk profiles. For instance, can a failure result in significant harm to patients? If yes, your
medical device belongs to a higher-risk category, so you may follow a tighter regulatory framework.
At the same time, other healthcare software solutions like wellness apps are not obvious to fall
under the rules established by medical device regulators. That is because they serve more as
informational tools rather than the options used to monitor medical conditions. But what does
it mean?
You can take the relevant data as an indicator to check out. However, you cannot use it for diagnosis
or professional clinical management of patients’ symptoms. Thus, both developers and investors
can focus on creating such types of devices since they are easy to copy. Also, they offer less
practical use cases in terms of medical care.
Finally, when it comes to medical device SaMD regulations, there is a need to mention the United
Kingdom’s Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. This institution has developed
guidance supporting innovation regarding machine learning applications called Good Machine Learning Practice for Medical Device Development.
Although this resource is quite short, it is crucial for reading by those who aim to create
a SaMD product using ML algorithms.
Example of software as a medical device
When speaking of SaMD, you should refer to the group of medical device tools that satisfy
all the requirements provided by the SaMD regulations. At the same time, Software as a
Medical Device product not only stays on top of other different connecting technologies but
also leverages their advantages significantly. Such technologies may involve various
sensors; connectivity like LTE, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth; robust mobile devices like smartphones
and tablets; and a cloud environment that allows for distributed processes and information
storage.
With excellent data mobility offered by the innovative tools from the SaMD category, medical
facilities can deliver better treatment options compared to using a traditional medical device.
Also, there is an opportunity to combine your SaMD solution with cutting-edge tech trends, including
artificial intelligence (AI) and big data. That makes it possible to obtain unique clinical insights.
After all, modern medical device SaMD products can strengthen care delivery and administration,
cut down costs, and lead to improved health outcomes.

Below, we have analyzed some most popular examples of applying Software as a Medical Device tools:
Screening & Diagnosis
Because of the ability to leverage complex algorithms, SaMD products can precisely predict
the risk of potential chronic diseases and assist in making proper treatment decisions.
A good, real-life example is a Genetesis’ biomagnetic imaging device that is very similar to a traditional MRI scanner. The
particular tool evaluates the electromagnetic activity in patients’ bodies more deeply. In this
case, SaMD benefits from the power of machine learning (ML) algorithms to obtain multiple features
from gathered information. That helps radiologists analyze anomalies that other diagnostics tools,
such as an electrocardiogram can miss.
Monitoring & Alerting
You can design Software as a Medical Device system to utilize wearable sensors collecting
numerous vital signs. These signs are later tracked using software for medical purposes.
With SaMD software tools, healthcare organizations can monitor and use the relevant data to
provide targeted recommendations and alerts for doctors and their patients.
For example, a well-known digital therapeutics company, Propeller Health, aims to treat key respiratory disorders like asthma
or chronic obstructive pulmonary (COPD) with actual hardware that is software-enabled thanks
to Bluetooth technology.
Their small sensors can be easily attached to patients’ inhalers for tracking triggers and symptoms.
Such inhalers, which are wired using a specific Bluetooth transmitter, “speak” to patients’ smartphones.
Also, they can send personalized feedback, updates, and information to patients and doctors.
Thus, physicians can analyze this data and know the frequency of attacks patients suffer, and
define the environmental factors causing the relevant distress.
Chronic Condition & Disease Management
Software as a Medical Device solutions enable patients and physicians to track and interpret
valuable health information, assess the current healthcare situation, and make treatment
plans more efficient.
For instance, let’s take a look at Eli Lilly’s Go Dose, a top-notch diabetes management mobile application
for Humalog (an insulin the company develops) users. The app can be utilized at home and within
a clinical environment to assist in reviewing, analyzing, and evaluating historical blood glucose
test values. That is crucial for type 2 diabetes mellitus management.
One of the key app’s medical functions is the ability to provide dosage recommendations for meals
depending on patients’ blood glucose levels. Such a feature helps patients and doctors ensure
more effective management of their diseases.
Digital Theraupetics
Using SaMD is also essential for therapeutic purposes, particularly to treat or mitigate
critical illnesses. That is because tools representing the SaMD category generate
highly-relevant clinical information from other traditional medical devices, a
general-purpose computing platform, and even other available non-medical computing platforms
that deal with therapy provision to human bodies.
In the case of SaMD digital therapeutics,
the best possible example is
Pear Therapeutics. This company
creates software-based therapies for those who suffer from psychiatric and neurologic
conditions. So, instead of swallowing pills or taking injections, patients struggling with
substance disorders obtain software-based treatment. reSET, the leading product of Pear
Therapeutics, delivers cognitive behavioral therapy. It assists patients in abstaining from
alcohol and drug usage during the treatment process.
Moreover, reSET offers a dashboard that allows doctors to explore their patients’ substance use,
triggers, and many more to come up with more efficient treatment options.
Software development for SaMD
When most software engineers prefer an agile methodology, which is more flexible because of
a continuous loop of iteration, a lot of SaMD companies remain the players in the typical
medical device market. They claim that applying agile approaches is impossible due to strict
regulations. No doubt, these rules are written in a linear style that is suitable for a
waterfall model. But utilizing agile product development and maintaining the necessary
compliance are also real, despite the current standards.
According to the IEC 62304 process standard, there are five critical processes that each SaMD
development company should implement during the software lifecycle. Let’s analyze them.
Software Development Process
SaMD software development starts with appropriate planning and ends with product release. But between the relevant points, you must take some essential steps:
- Analyzing software requirements
- Designing software architecture
- Implementing and verifying software units
- Integrating software
- Testing a software system
However, after releasing your SaMD solution, your responsibilities will not end. That is because you should maintain it effectively and address emerging issues.
Software Maintenance Process
The particular process involves the following three elements:
- Creating a software maintenance plan
- Analyzing problems and modifications
- Applying modifications
Besides, before creating a new process to maintain your Software as a Medical Device, you should explore your current complaint-handling process. Because of the potential overlap between them, there may be no need for you to establish two separate processes.
Software Risk Management Process
The risk management requirements provided by the IEC 62304 standard correlate with the rules mentioned in ISO 14971, a specific international standard related to the risk management of medical devices. In this case, the process includes:
- Analyzing the software’s potential contribution to hazardous situations
- Creating risk control measures
- Verifying risk control measures
- Managing the risk of software changes
Software Configuration Management Process
You may consider the software configuration of your SaMD product’s accounting. That is because you keep track of all critical things required to recreate a solution, which is vital for effective release management. The SaMD software configuration management process covers:
- Identifying configuration
- Controlling changes
- Configuration status accounting
The numerous SaMD development companies utilize a specific configuration matrix to ensure the best possible configuration management.
Software Problem Resolution Process
Since you may encounter various types of issues during the SaMD software lifecycle, you should have some problem-resolution processes. Here is a general outline of critical steps for them:
- Preparing problem reports
- Investigating the problems
- Advising relevant parties
- Using a change control process
- Maintaining records
- Analyzing issues for trends
- Verifying software problem resolution
- Testing documentation contents
The key trends in SaMD and connected health
Since SaMD is among the most rapidly growing sectors, a large number of talented software developers are involved in creating life-changing medical devices. For instance, the latest trends related to SaMD software development are the following:

Wearable Devices
Although wearables have been already used for some years and in multiple industries, they have started providing more advanced data collection. That can be proved by the latest versions of Apple Watches. And despite being popular among fitness lovers, up-to-date wearables may become robust medical equipment that assists in improving patient safety and overall care. One of the best examples is providing doctors with an opportunity to remotely monitor their patient’s conditions, including blood pressure and heart rate.
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
Healthcare providers may find it challenging to manage all the medical information gathered
by SaMD in a useful and convenient way for both clinicians and their patients. That is where
the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) comes in handy. IoMT serves as a digital technology
platform that connects medical devices and existing healthcare systems. It allows for
sharing data in the right places, which, in turn, promotes more accurate decision-making.
Thus, many companies in the medical device market prefer creating partnerships with healthcare
systems vendors, which is vital for better information sharing.
Telehealth
The global coronavirus pandemic has demonstrated the need to change the approaches to providing medical care and consultations. And although some telemedicine solutions have already existed, the COVID-19 crisis encouraged hardware medical device manufacturers to focus on developing SaMD solutions that would be more advanced and user-friendly. After all, SaMD plays an essential role when it comes to remote data collection. That is because connected mobile devices are an integral part of healthcare monitoring and decision-making.
Final thoughts
To conclude, the Software as a Medical Device concept is quite complex. However, it will
continue to evolve and expand its influence on the entire digital health industry.
But at the same time, you should remember some gray areas associated with rules and guidelines
for SaMD software development, even though they may be resolved in the next few years. Also,
the cybersecurity issue is among those requiring a lot of work to address it. And finally, a learning curve
for engineers new to the medical device software industry often appears steep.
In parallel, engaging in
EHR development
is a critical aspect that complements the SaMD ecosystem, enhancing patient data management and interoperability.
On the other hand, SaMD can create immense opportunities and bring excitement to each healthcare
provider benefiting both doctors and patients. Therefore, we hope this particular guide will
help you build safe and effective software that will enhance patient safety, improve clinical
management, and ensure better health outcomes. Having the right tech tools and an experienced
partner, you can develop high-quality SaMD solutions increasing the numerous patients’ quality
of life.
Are you considering building top-notch Software as a Medical Device tool and contributing to
the digital transformation of the healthcare industry? Contact us today, and we will discuss
the opportunities for cooperation on your SaMD project.
